Turn on Render on Demand
Prerequisite
If you want to fully leverage the power of ROD, using a ZK model object
like ListModel is necessary.
ROD actually brings a performance boost on both the client-side and
server-side. However, if you use forEach to populate Rows or
Listitems, the components will be all in memory, which does not give you
any performance benefits on the server-side. (The client-side still
enjoys a boost.)
Notice that you can enable this feature in different scopes.
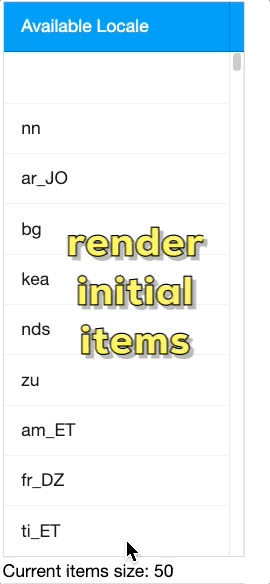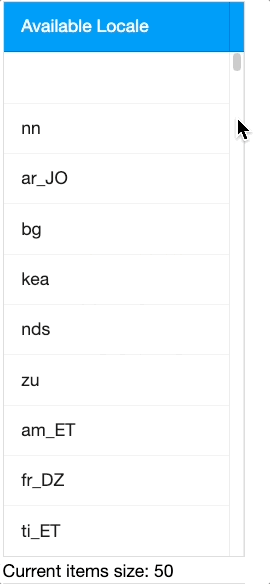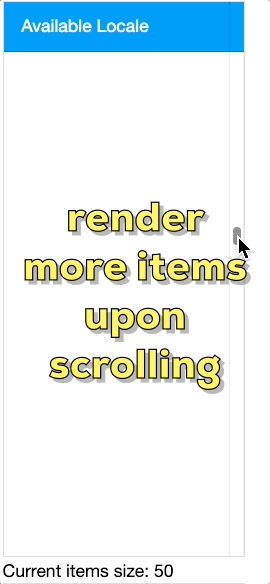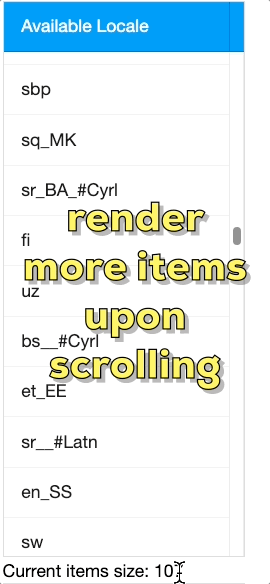
Grid
If you want to enable Grid ROD for the whole application, you can
specify a library property called org.zkoss.zul.Grid
rod with true. For example, specify the following in zk.xml:
<library-property>
<name>org.zkoss.zul.grid.rod</name>
<value>true</value>
</library-property>
Or, if you prefer to enable it for a particular page, then specify
true to a page’s attribute called
org.zkoss.zul.Grid rod, such as
<custom-attributes org.zkoss.zul.grid.rod="true" scope="page"/>
Or, if you prefer to enable it for all descendant grids of a particular
component, then specify true to the component’s attribute. You can
enable it for a subset of the descendant grids. For example,
<window>
<custom-attributes org.zkoss.zul.grid.rod="true"/> <!-- enable it for descendant grids of window -->
<grid ...>
..
</grid>
<div>
<custom-attributes org.zkoss.zul.grid.rod="false"/> <!-- disable it for descendant grids of div -->
<grid ...>
..
</grid>
..
</div>
</window>
Fixed Viewport is Required
Note that Grid ROD will not work unless the Grid is configured with a limited viewport, so the user can see only a portion of rows; i.e. you have to set one of the following attributes:
heightvflexmold="paging"visibleRows
Specifies the number of rows rendered
[default: 100]
[inherit: true]
Specifies the minimum number of rows rendered on the client. It is only considered if Grid is using live data (org.zkoss.zul.Grid#setModel(ListModel)) and not using paging mold (org.zkoss.zul.Grid#getPagingChild()).
<custom-attributes org.zkoss.zul.grid.initRodSize="30"/>
Listbox
If you want to enable Listbox ROD for the whole application, you can
specify a library property called
org.zkoss.zul.Listbox rod with true. For example,
specify the following in zk.xml:
<library-property>
<name>org.zkoss.zul.listbox.rod</name>
<value>true</value>
</library-property>
Or, if you prefer to enable it for a particular page, then specify
true to a page’s attribute called
org.zkoss.zul.Listbox rod, such as
<custom-attributes org.zkoss.zul.listbox.rod="true" scope="page"/>
Or, if you prefer to enable it for all descendant listboxs of a
particular component, then specify true to the component’s attribute.
And, you can enable it for a subset of the descendant listboxs. For
example,
<window>
<custom-attributes org.zkoss.zul.listbox.rod="true"/> <!-- enable it for descendant listboxs of window -->
<listbox ...>
..
</listbox>
<div>
<custom-attributes org.zkoss.zul.listbox.rod="false"/> <!-- disable it for descendant listboxs of div -->
<listbox ...>
..
</listbox>
..
</div>
</window>
Fixed Viewport is Required
Note that Listbox ROD will not work unless the Listbox is configured with a limited viewport, so the user can see only a portion of listitems; i.e. you have to set one of the following attributes:
heightvflexrowsmold="paging"
Specifies the number of items rendered
[default: 100]
[inherit: true]
Specifies the number of items rendered when the Listbox first renders.
It is used only if live data
(org.zkoss.zul.Listbox#setModel(ListModel))
and not paging (mold="paging").
<custom-attributes org.zkoss.zul.listbox.initRodSize="30"/>
Tree
To turn off ROD for a tree, you need to specify org.zkoss.zul.tree.initRodSize with -1:
<custom-attributes org.zkoss.zul.tree.initRodSize="-1"/>
Limitation
hflex="min" has a not-resizing limitation,
so if you specify it on a <grid>/<column> (<listbox>/<listheader>, or <tree>/<treecol>), a component doesn’t
resize the column when you scrolls down to see a wider item. Because the
wider item is not rendered initially for render-on-demand. At the moment
of calculating the width, the component doesn’t count the wider item
into width calculation.
Grid and Listbox will enlarge their columns when you scroll down and render a wider item.
How ROD Works Internally
Render on Demand (ROD) is a sophisticated optimization technique in ZK Enterprise Edition that fundamentally changes how large datasets are handled in web applications. Understanding its internal mechanism helps developers leverage this feature effectively.
Technical Architecture
ROD operates through a multi-layer optimization strategy that minimizes resource usage across the entire data processing pipeline:
- Browser DOM (D): Rendered DOM elements visible to users
- Server Component (C): ZK server-side component instances
- Server ListModel (L): Data model layer
- Database Record (R): Actual data records in storage
Data Flow Optimization Levels
- No ROD (Live Data)
D = C = L = R- All data layers are equal in size- Every database record creates a server component and DOM element
- Memory usage scales linearly with dataset size
- ROD Enabled
D = C < L = R- Components and DOM elements are minimized- Only visible components are rendered while full dataset remains in ListModel
- Significant reduction in browser memory and rendering time
- Custom ListModel with ROD
D = C < L < R- Maximum optimization across all layers- ListModel acts as a smart cache, loading data chunks on demand
- Optimal for extremely large datasets (millions of records)
Rendering Process
When ROD is active, ZK employs a sophisticated viewport-based rendering strategy:
- Initial Render: Creates required Row(s)/Listitem(s) on the server for visible viewport
- DOM Generation: Renders only the corresponding widgets and DOM elements actually needed in browser
- Scroll Handling: Removes previous components when scrolling and creates new ones for newly visible items
- Padding Simulation: Uses
[uuid]-tpadand[uuid]-bpadelements to simulate non-rendered items and maintain proper scrollbar behavior
This approach dramatically reduces both server-side component creation and client-side DOM manipulation.
Performance Benefits
ROD provides substantial performance improvements across multiple dimensions:
Memory Optimization
Server-Side Benefits:
- Maintains only visible component instances in memory
- Eliminates memory bottlenecks for large datasets
- Reduces garbage collection pressure
Browser-Side Benefits:
- Minimizes DOM tree size regardless of dataset size
- Prevents browser memory exhaustion with large lists
- Maintains responsive user interface
Rendering Performance
Initial Load:
- Faster page load times as only visible content is rendered
- Reduced network payload for initial page response
- Improved perceived performance for users
Scrolling Performance:
- Smooth scrolling even with millions of records
- Constant memory usage during navigation
- No performance degradation as dataset grows
Network Efficiency
- Only necessary data chunks are transmitted to browser
- Reduced bandwidth usage for large datasets
- Optimized server responses through intelligent caching
ROD vs Live Data vs Custom ListModel Comparison
The following diagram illustrates how ROD optimizes the data processing pipeline across different layers:
Browser Server Server Database
┌─────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ DOM │ │ Component │ │ ListModel │ │ Record │
│ D │ │ C │ │ L │ │ R │
└─────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘
• No ROD (Live Data): D = C = L = R
• ROD Enabled: D = C < L = R
• Custom ListModel+ROD: D = C < L < R
Optimization Strategy Breakdown
Live Data (No ROD):
- Creates outer DOM elements for all Row/Listitem initially
- Renders child components progressively during scrolling
- Never removes components, continuously adds DOM elements
- No top/bottom padding optimization
ROD Enabled:
- Creates only required Row(s)/Listitem(s) on server
- Renders only necessary widgets and DOM elements in browser
- Removes previous components when scrolling
- Uses padding elements (
[uuid]-tpad,[uuid]-bpad) to simulate non-rendered items
Custom ListModel with ROD:
- Further optimizes by minimizing data in the ListModel layer
- Implements smart caching that loads data chunks on demand
- When desired entry not in cache, loads associated data range
- Maximum optimization for extremely large datasets